What is Semaglutide
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1): The Hormone That Tells Your Brain You're Full
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) is a hormone naturally released by your gut to signal your brain that it's time to stop eating. Isn't the human body fascinating? You might wonder, "If our bodies make this hormone, why do we need a synthetic version?" Let's dive into a quick lesson on gastrointestinal (GI) anatomy and physiology to explain.
When you enjoy a meal rich in protein, carbohydrates (yes, your body needs carbs), and fats, digestion begins as soon as you start chewing. Enzymes in your saliva start breaking down carbs and fats, preparing them for your stomach. After the food passes through your stomach, it enters the small intestine. This journey involves about twenty feet of small intestine before the GLP-1 magic happens.
At the end of the ileum and into the large intestine, there are specialized cells in your intestinal wall called L-cells. These cells have chemosensors that detect the presence of food. Imagine these L-cells giving your hamburger a "high five" as it passes by. This interaction prompts the L-cells to release GLP-1, signaling your brain that you’re not hungry. I imagine it looking something like this:
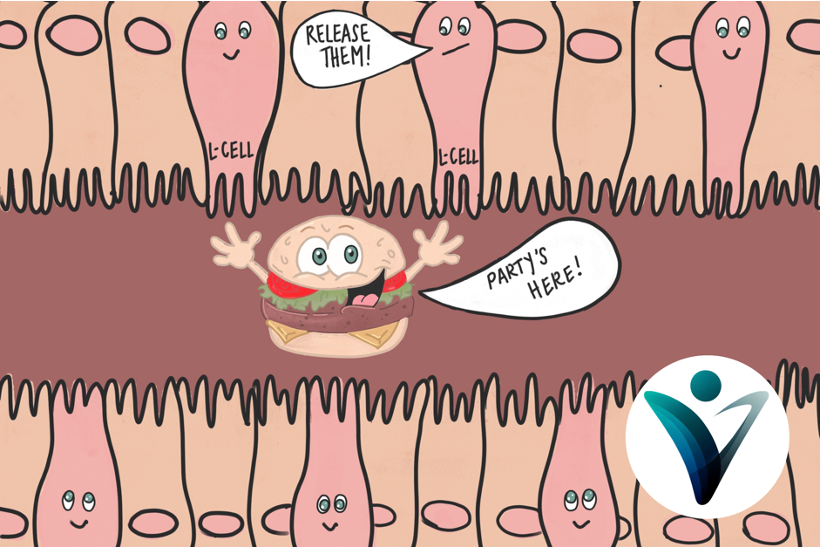
However, there’s a catch: it takes 4-6 hours for your food to reach this part of your gut, and the GLP-1 hormone released has a half-life of just 4 minutes. In other words, the natural hormone that tells your brain you’re full takes hours to activate and lasts only minutes.
This is where synthetic GLP-1, like semaglutide, comes in. Without waiting for digestion, semaglutide tells your brain that you're not hungry, and this effect lasts for an entire week. This mechanism is how semaglutide works and why it can be incredibly helpful in your weight loss and wellness journey.
We are here to answer any questions and excited to support you in reaching your goals!
Resources:
- DrBeen Medical Lecture
- Zhao X, Wang M, Wen Z, Lu Z, Cui L, Fu C, Xue H, Liu Y, Zhang Y. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: Beyond Their Pancreatic Effects. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Aug 23;12:721135. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.721135. PMID: 34497589; PMCID: PMC8419463.
